
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved from monolithic systems to highly modular, task-optimized models. As technology advances, the need for specialized AI architectures tailored to unique tasks becomes more pronounced. The image presented above showcases eight specialized AI models, each crafted to solve distinct computational problems with enhanced performance, precision, and efficiency. These models—LLM, LCM, LAM, MoE, VLM, SLM, MLM, and SAM—represent the vanguard of AI system design.
Let’s dive into the architecture and function of each model.
1. LLM: Large Language Model
Pipeline:
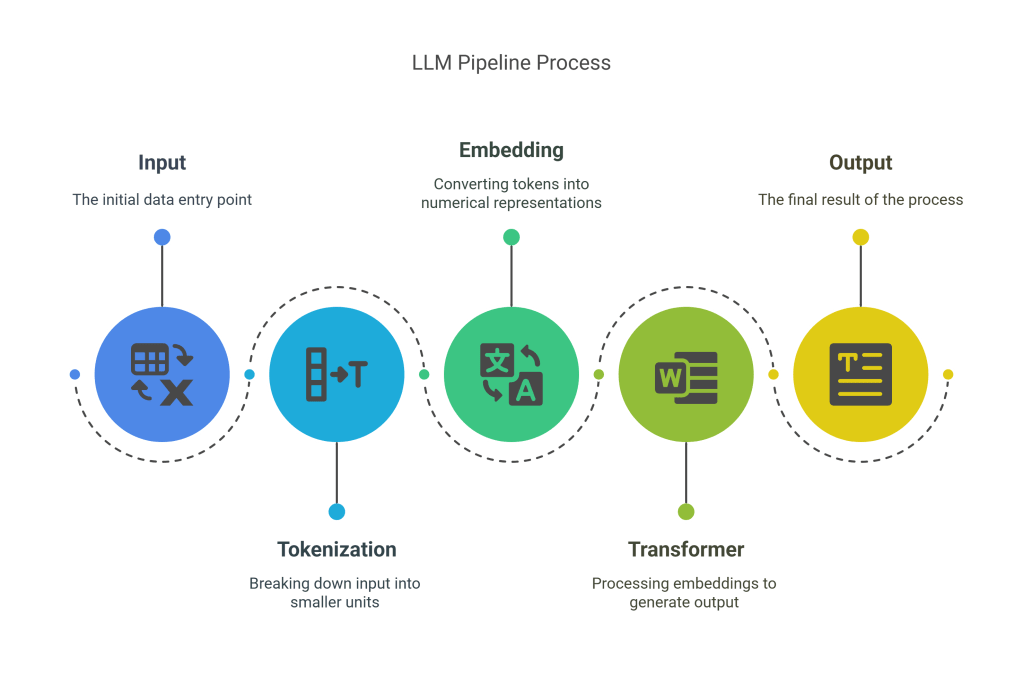
- Input → Tokenization → Embedding → Transformer → Output
Description:
The Large Language Model (LLM) is the backbone of modern generative AI like GPT, Claude, and Gemini. Its architecture relies on tokenizing the input (text), transforming these tokens into vector embeddings, processing them through multiple transformer layers, and producing output predictions.
Components:
- Tokenization: Converts input text into a sequence of tokens.
- Embedding Layer: Maps tokens to high-dimensional vectors.
- Transformer: The core engine that uses self-attention mechanisms for context understanding.
- Output: Generates text, predictions, or other token-based results.
Applications:
- Chatbots
- Text generation
- Code synthesis
- Sentiment analysis
2. LCM: Latent Concept Model
Pipeline:
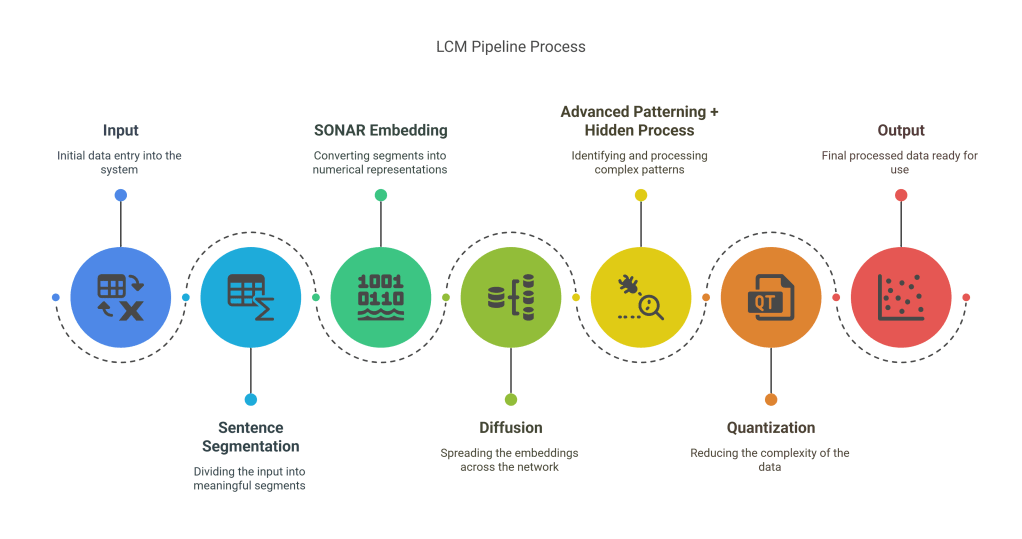
- Input → Sentence Segmentation → SONAR Embedding → Diffusion → Advanced Patterning + Hidden Process → Quantization → Output
Description:
The Latent Concept Model (LCM) emphasizes understanding sentence-level semantics and latent patterns that are not directly observable in raw data. It introduces a diffusion-based architecture which enables semantic interpolation in latent space.
Components:
- Sentence Segmentation: Splits text into coherent semantic units.
- SONAR Embedding: Context-aware vector representation.
- Diffusion: A probabilistic method to refine latent representations.
- Advanced Patterning + Hidden Process: Extracts deeper relationships.
- Quantization: Converts latent outputs to usable discrete representations.
Applications:
- Document summarization
- Cognitive reasoning tasks
- Latent space interpolation in creativity tools
3. LAM: Language Action Model
Pipeline:

- Input → Perception System → Intent Recognition → Task Breakdown → Neuro-Symbolic Integration + Memory System → Action Planning → Action Execution → Feedback Integration → Output
Description:
The LAM is tailored for cognitive agents that simulate human-like decision-making. This architecture combines neuro-symbolic reasoning with memory systems, enabling it to comprehend intent and execute contextually relevant actions.
Components:
- Perception System: Interprets environmental or linguistic input.
- Intent Recognition: Decodes user or agent goals.
- Neuro-Symbolic Integration: Blends symbolic logic with neural methods.
- Memory System: Stores context for long-term planning.
- Feedback Integration: Allows real-time adaptation.
Applications:
- Robotics
- Digital assistants
- Cognitive automation
- Planning systems
4. MoE: Mixture of Experts
Pipeline:
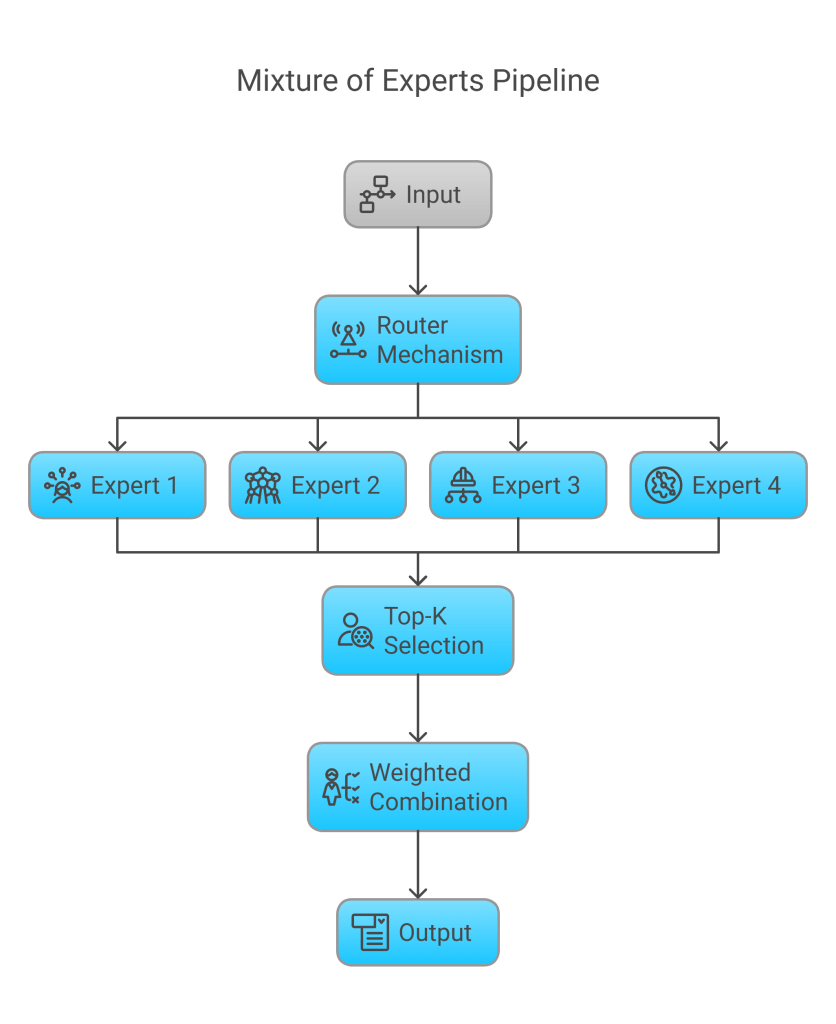
- Input → Router Mechanism → Expert 1, 2, 3, 4 → Top-K Selection → Weighted Combination → Output
Description:
The Mixture of Experts (MoE) model introduces scalability by routing parts of the input to specialized sub-models (experts). This dynamic selection ensures efficient computation without sacrificing output quality.
Components:
- Router Mechanism: Assigns tasks to relevant experts.
- Experts (1–4): Specialized neural networks trained on specific data patterns.
- Top-K Selection: Chooses top performing experts for a task.
- Weighted Combination: Aggregates outputs proportionally.
Applications:
- Efficient large-scale models (e.g., GShard, Switch Transformer)
- Multilingual and multi-domain tasks
- Adaptive neural computation
5. VLM: Vision-Language Model
Pipeline:

- Image Input + Text Input → Vision Encoder + Text Encoder → Projection Interface → Multimodal Processor → Language Model → Output Generation
Description:
VLMs integrate visual and linguistic understanding, enabling AI to generate textual descriptions for images and vice versa. These models represent the convergence of computer vision and NLP.
Components:
- Vision Encoder: Extracts features from images.
- Text Encoder: Processes language inputs.
- Projection Interface: Aligns vision and text in a shared latent space.
- Multimodal Processor: Merges modalities contextually.
- Language Model: Generates text output based on visual context.
Applications:
- Image captioning
- Visual question answering
- Multimodal chatbots
- Accessibility tools
6. SLM: Small Language Model
Pipeline:

- Input Processing → Compact Tokenization → Optimized Embeddings → Efficient Transformer → Model Quantization/Memory Optimization → Edge Deployment → Output Generation
Description:
SLM refers to language models optimized for deployment on edge devices (phones, embedded systems). These models balance performance and resource usage through aggressive optimization and quantization.
Components:
- Compact Tokenization: Efficient representation of inputs.
- Optimized Embeddings: Reduce parameter count.
- Efficient Transformer: Lightweight transformer variant.
- Edge Deployment: Capable of running on low-power hardware.
Applications:
- Offline assistants
- Embedded AI in smart devices
- Privacy-first AI tasks
7. MLM: Masked Language Model
Pipeline:

- Text Input → Token Masking → Left Context + Right Context → Bidirectional Attention → Masked Token Prediction → Feature Representation
Description:
MLMs like BERT use a masked-token approach to learn bidirectional representations of text. By predicting missing tokens, the model develops a deep understanding of context from both directions.
Components:
- Token Masking: Randomly hides parts of the input.
- Bidirectional Attention: Processes context from both sides.
- Masked Token Prediction: Predicts missing information.
- Feature Representation: High-quality embeddings for downstream tasks.
Applications:
- Text classification
- Named entity recognition
- Text similarity
- Search engines
8. SAM: Segment Anything Model
Pipeline:
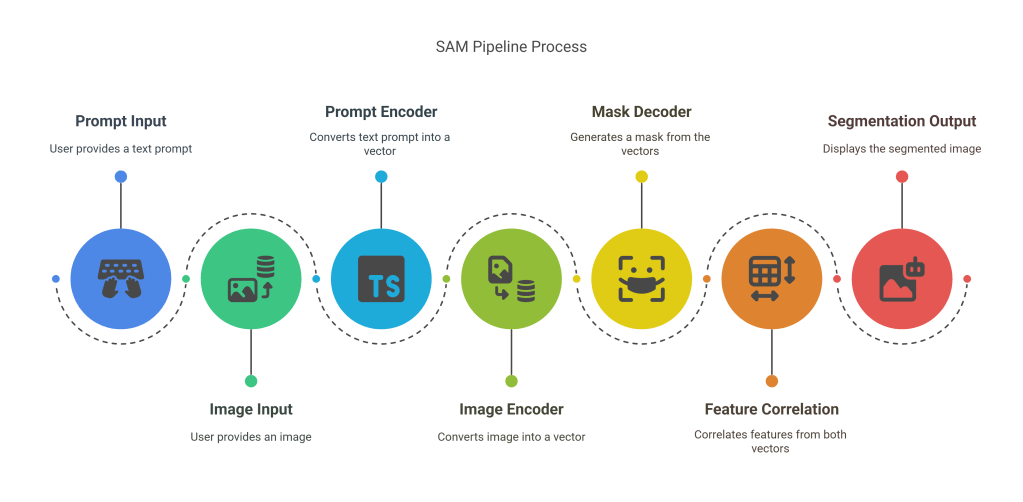
- Prompt Input + Image Input → Prompt Encoder + Image Encoder → Mask Decoder + Feature Correlation → Segmentation Output
Description:
The SAM model by Meta AI is designed for universal image segmentation. With a promptable interface, SAM enables precise segmentation of any object in an image.
Components:
- Prompt Encoder: Translates user prompts (click, text, etc.) into vector signals.
- Image Encoder: Processes the visual data.
- Mask Decoder: Predicts segmentation boundaries.
- Feature Correlation: Aligns prompt and image features.
Applications:
- Medical imaging
- AR/VR segmentation
- Video editing
- Robotics vision systems
Comparative Analysis
| Model | Modality | Use Case | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLM | Text | Text generation | Contextual understanding |
| LCM | Text | Pattern recognition | Latent semantic mapping |
| LAM | Multi | Decision-making | Planning + memory |
| MoE | Any | Scalability | Sparse activation |
| VLM | Image + Text | Multimodal tasks | Vision-language alignment |
| SLM | Text | Edge AI | Compact & efficient |
| MLM | Text | Contextual prediction | Bidirectional training |
| SAM | Image | Segmentation | Universal prompting |
Real-World Use Cases
AI in Healthcare:
- SAM helps radiologists with automatic organ and tumor segmentation.
- LLM supports medical documentation and summarization.
- LCM is used in interpreting medical research papers via latent semantic understanding.
AI in Business:
- MoE scales enterprise AI models for handling customer queries across domains.
- LAM powers AI agents in task automation and intelligent CRMs.
- SLM powers smart devices with low-bandwidth AI models for customer interactions.
AI in Creative Industries:
- VLM enables creators to generate images from descriptions.
- MLM is fine-tuned for sentiment tagging in user reviews and content curation.
Future Trends
- Hybrid Architectures: Expect to see more models combining strengths—like LAM + MoE for scalable intelligent agents.
- Edge AI Growth: With the explosion of IoT, SLMs will become dominant.
- Multimodal Integration: VLMs and SAMs will evolve into more generalized models capable of understanding images, video, and audio.
- Autonomous Agents: LAM will be crucial for robotics and autonomous systems requiring high-level cognition.
Conclusion
These eight specialized AI models represent the diversity and specialization required to push the boundaries of what machines can do. Each is designed with a specific philosophy and engineering principle to optimize for scale, efficiency, context, or multimodality. As AI applications continue to expand, so will the need for hybrid, modular, and intelligent architectures that bring together the best of each.
Understanding these models not only helps developers choose the right tool for the task but also inspires innovation in combining and evolving them for next-generation AI systems.
Discover more from SkillWisor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
