
Introduction
The convergence of artificial intelligence and mobile computing has reached a pivotal moment with the emergence of edge AI architecture in smartphones. Unlike traditional cloud-based AI solutions that rely on remote servers for processing, edge AI brings computational intelligence directly to the device, enabling real-time decision-making, enhanced privacy, and reduced latency. This architectural paradigm shift is transforming how smartphones interact with users and process data, creating unprecedented opportunities for intelligent mobile applications.
Edge AI represents a fundamental departure from the client-server model that has dominated mobile computing for over a decade. By embedding AI processing capabilities directly into smartphone hardware, manufacturers are enabling devices to perform complex machine learning tasks without requiring constant connectivity to external servers. This approach addresses critical limitations of cloud-based AI, including network dependency, privacy concerns, and latency issues that can impair user experience.
Core Components of Edge AI Architecture

Neural Processing Units (NPUs)
At the heart of edge AI architecture lies the Neural Processing Unit, a specialized chip designed specifically for accelerating machine learning computations. Modern smartphones integrate dedicated NPUs alongside traditional CPU and GPU architectures, creating a heterogeneous computing environment optimized for AI workloads. These units feature parallel processing capabilities with thousands of small cores designed to handle the matrix operations fundamental to neural network inference.
The NPU architecture typically includes specialized memory hierarchies, optimized data pathways, and hardware-accelerated operations for common AI functions such as convolution, pooling, and activation functions. Leading smartphone manufacturers have developed custom NPU designs, including Apple’s Neural Engine, Qualcomm’s Hexagon DSP with AI extensions, and Huawei’s Kirin NPU, each offering unique advantages in terms of performance, power efficiency, and supported AI frameworks.
AI Software Stack
The software stack supporting edge AI in smartphones consists of multiple layers, each serving specific functions in the AI processing pipeline. At the foundation lies the hardware abstraction layer, which provides standardized interfaces for accessing NPU capabilities across different chip architectures. This layer ensures that AI applications can leverage hardware acceleration without requiring platform-specific optimizations.
Above the hardware abstraction layer sits the AI runtime environment, which manages model execution, memory allocation, and resource scheduling. Popular runtime environments include TensorFlow Lite, Core ML, and NNAPI (Neural Networks API), each offering different advantages in terms of performance optimization, model compatibility, and development tools. These runtimes incorporate sophisticated optimization techniques such as quantization, pruning, and operator fusion to maximize inference speed while minimizing memory footprint and power consumption.
Model Optimization Techniques
Edge AI architectures employ various optimization techniques to adapt complex AI models for mobile deployment. Quantization reduces model size and computational requirements by converting 32-bit floating-point weights to lower precision formats such as 8-bit integers or even binary representations. This technique can achieve 4x reduction in model size with minimal accuracy loss, making it essential for resource-constrained mobile environments.
Pruning eliminates redundant neural network connections, reducing both model size and computational complexity. Structured pruning removes entire neurons or channels, while unstructured pruning eliminates individual weights based on magnitude or importance metrics. Knowledge distillation transfers learning from large, complex models to smaller, more efficient architectures suitable for mobile deployment, preserving much of the original model’s accuracy while dramatically reducing computational requirements.
Hardware Architecture Design
Heterogeneous Computing Integration
Modern edge AI architectures embrace heterogeneous computing principles, distributing AI workloads across multiple processing units based on their specific strengths. The central processing unit handles control flow and sequential operations, while the graphics processing unit accelerates parallel computations such as image preprocessing and certain neural network layers. The dedicated NPU focuses on core AI inference tasks, optimizing for the specific computational patterns common in machine learning workloads.
This heterogeneous approach requires sophisticated scheduling algorithms that can dynamically allocate AI tasks to the most appropriate processing unit based on current system conditions, power constraints, and performance requirements. Advanced smartphones implement hardware-aware scheduling that considers factors such as thermal state, battery level, and concurrent application demands when distributing AI workloads.
Memory Hierarchy Optimization
Edge AI architectures feature carefully designed memory hierarchies that balance performance, power efficiency, and cost considerations. High-bandwidth memory interfaces ensure rapid data movement between processing units and system memory, while specialized on-chip caches reduce memory access latency for frequently used model parameters and intermediate computations.
Some advanced designs incorporate dedicated AI memory pools with optimized access patterns for neural network operations. These memory subsystems feature wide data buses, high-speed interfaces, and intelligent prefetching mechanisms that anticipate data requirements based on model execution patterns. Memory compression techniques further extend effective capacity, allowing larger models to fit within available memory constraints.
Thermal and Power Management
Edge AI processing generates significant heat and consumes substantial power, necessitating sophisticated thermal and power management systems. Modern smartphones implement dynamic frequency scaling that adjusts processing unit clock speeds based on thermal conditions and performance requirements. Thermal throttling prevents overheating by temporarily reducing AI processing intensity when device temperature exceeds safe thresholds.
Power management systems employ predictive algorithms that anticipate AI workload patterns and adjust system configuration accordingly. These systems can preemptively reduce background processing, adjust display settings, or defer non-critical AI tasks to preserve battery life during intensive AI operations. Advanced power gating techniques selectively disable unused portions of AI processing units, minimizing idle power consumption.

AI Model Deployment Strategies
On-Device Model Storage
Edge AI architectures must efficiently store and manage multiple AI models on devices with limited storage capacity. Model compression techniques reduce storage requirements while maintaining acceptable accuracy levels. Delta compression stores only the differences between related models, enabling efficient storage of model variants or updates. Progressive model loading allows applications to start with lightweight base models and dynamically load additional components as needed.
Intelligent model caching systems automatically manage model lifecycle, removing unused models to free storage space while retaining frequently accessed ones. These systems consider factors such as model usage frequency, storage requirements, and user preferences when making caching decisions. Some implementations support model streaming, downloading specific model components on-demand from cloud repositories while maintaining core functionality offline.
Dynamic Model Selection
Advanced edge AI systems implement dynamic model selection mechanisms that choose the most appropriate model variant based on current device conditions and application requirements. These systems maintain multiple model variants optimized for different scenarios, such as high-accuracy models for critical tasks and lightweight models for battery-constrained situations.
Selection algorithms consider factors including available computational resources, battery level, thermal state, and required response time when choosing among available models. Machine learning techniques can predict optimal model selection based on historical usage patterns and current device state, continuously improving selection accuracy over time.
Privacy and Security Considerations
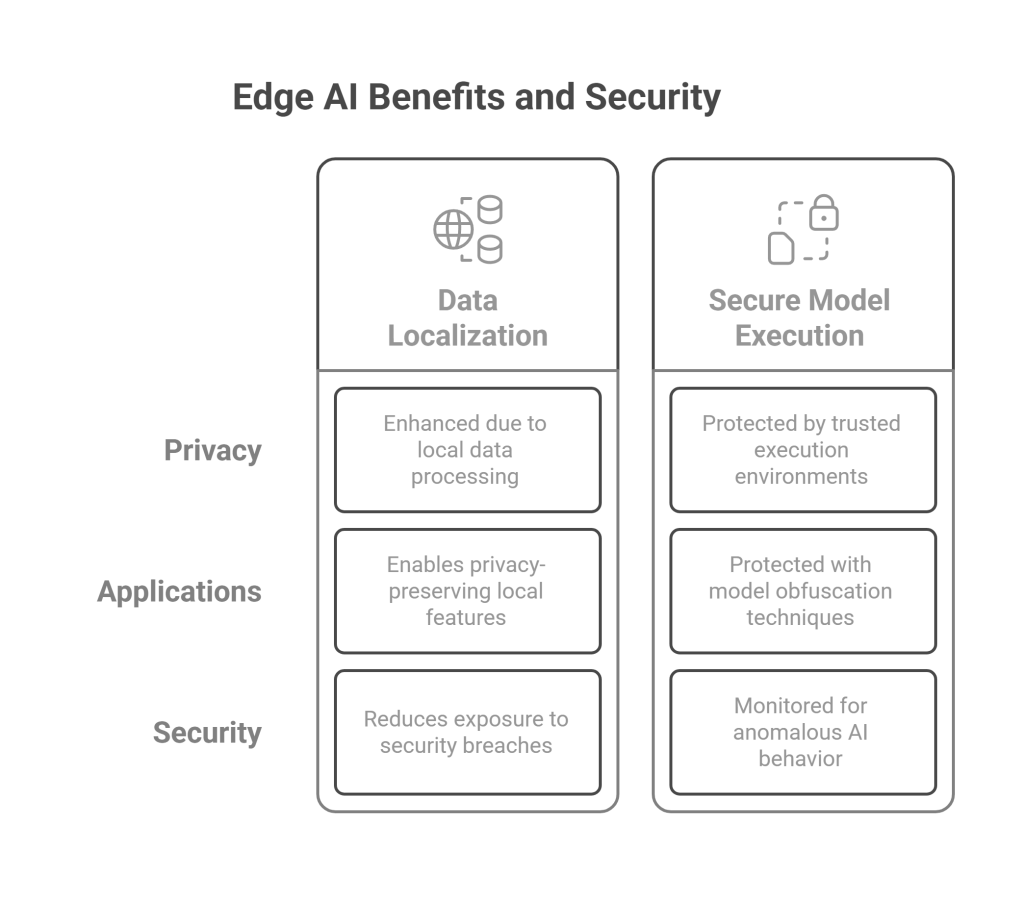
Data Localization Benefits
Edge AI architecture provides inherent privacy advantages by processing sensitive data locally on the device rather than transmitting it to remote servers. Personal information such as photos, voice recordings, and behavioral patterns remain on the device, reducing exposure to potential security breaches or unauthorized access. This approach aligns with growing privacy regulations and user expectations regarding data protection.
Local processing enables new categories of privacy-preserving applications that would be impractical with cloud-based architectures. Features such as real-time speech recognition, facial recognition, and behavioral analysis can operate without transmitting personal data, providing enhanced functionality while maintaining user privacy.
Secure Model Execution
Edge AI implementations incorporate various security measures to protect AI models and processing from malicious attacks. Trusted execution environments isolate AI processing from other system components, preventing unauthorized access to model parameters or intermediate computations. Hardware-based security features such as secure enclaves and cryptographic accelerators protect sensitive AI operations.
Model obfuscation techniques make it difficult for attackers to reverse-engineer AI models even if they gain access to device storage. Differential privacy mechanisms add controlled noise to model outputs, preventing inference attacks that might reveal sensitive information about training data. Runtime security monitoring detects anomalous AI behavior that might indicate security compromises or adversarial attacks.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Operator Fusion and Graph Optimization
Edge AI runtimes employ sophisticated graph optimization techniques to improve inference performance. Operator fusion combines multiple neural network operations into single, optimized kernels, reducing memory bandwidth requirements and improving cache utilization. Common fusion patterns include combining convolution with batch normalization and activation functions, or merging multiple element-wise operations.
Graph-level optimizations restructure neural network computation graphs to minimize memory usage and maximize parallelism. These optimizations might reorder operations, eliminate redundant computations, or introduce additional parallelism through layer splitting or pipelining. Advanced optimizers use machine learning techniques to automatically discover optimal graph transformations for specific hardware configurations.
Adaptive Precision Control
Modern edge AI systems implement adaptive precision control mechanisms that dynamically adjust numerical precision based on current requirements and constraints. Mixed-precision computation uses different numerical formats for different operations, employing high precision only where necessary for accuracy while using lower precision for less critical computations.
Dynamic precision scaling adjusts precision levels based on available computational resources, battery state, and accuracy requirements. These systems can gradually reduce precision during extended AI processing sessions to conserve power, or increase precision for critical operations requiring high accuracy. Machine learning algorithms predict optimal precision settings based on historical performance data and current system conditions.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Computer Vision Applications
Edge AI enables sophisticated computer vision applications that operate in real-time without cloud connectivity. Advanced camera systems leverage edge AI for computational photography features such as portrait mode, night mode, and scene optimization. These applications require real-time processing of high-resolution image data, making local processing essential for acceptable user experience.
Augmented reality applications represent another significant use case for edge computer vision. Real-time object detection, tracking, and scene understanding enable immersive AR experiences that respond instantly to environmental changes. Edge processing eliminates the latency that would make cloud-based AR applications impractical for interactive use cases.
Natural Language Processing
Edge AI architectures support sophisticated natural language processing applications including real-time speech recognition, language translation, and text analysis. Local speech processing enables voice assistants to respond quickly to user commands while maintaining privacy by avoiding transmission of audio data to remote servers. Advanced implementations support multiple languages and accents through specialized model variants.
Text analysis applications leverage edge AI for features such as sentiment analysis, content summarization, and intelligent text completion. These applications benefit from the low latency and privacy advantages of local processing while providing sophisticated language understanding capabilities previously available only through cloud services.
Personalization and Recommendation Systems
Edge AI enables highly personalized experiences through local learning and adaptation. Recommendation systems can analyze user behavior patterns locally, building detailed preference models without transmitting personal data to external servers. These systems continuously adapt to changing user preferences while maintaining privacy through local data processing.
Adaptive user interfaces leverage edge AI to optimize application layouts, feature accessibility, and interaction patterns based on individual usage patterns. Machine learning algorithms analyze user behavior in real-time, adjusting interface elements to improve usability and efficiency for each specific user.
Challenges and Limitations

Resource Constraints
Despite significant advances in mobile hardware, edge AI still faces substantial resource constraints compared to cloud-based alternatives. Limited memory capacity restricts the size and complexity of AI models that can be deployed on mobile devices. Processing power limitations affect inference speed, particularly for compute-intensive models such as large language models or high-resolution image processing networks.
Battery life represents another critical constraint, as AI processing can quickly drain mobile device batteries. Balancing AI capability with battery life requires careful resource management and optimization techniques. Thermal constraints further limit sustained AI processing performance, as prolonged high-intensity computation can cause devices to overheat and throttle performance.
Model Accuracy Trade-offs
The optimization techniques required for edge deployment often involve accuracy trade-offs compared to full-scale cloud models. Quantization, pruning, and compression can reduce model accuracy, particularly for complex tasks requiring high precision. Balancing model size, processing speed, and accuracy remains a significant challenge in edge AI deployment.
Limited training data availability on mobile devices can also affect model accuracy over time. While some edge AI systems support on-device learning and adaptation, the limited computational resources and data availability compared to cloud environments can restrict the effectiveness of local model improvements.
Future Trends and Developments
Advanced Hardware Integration
Future edge AI architectures will feature even tighter integration between AI processing units and other smartphone components. Neuromorphic computing architectures that mimic brain-like processing patterns promise significant improvements in power efficiency and learning capability. These architectures could enable continuous learning and adaptation while consuming minimal power.
Advanced memory technologies such as processing-in-memory and compute-near-data architectures will reduce data movement overhead, improving both performance and power efficiency. Three-dimensional chip integration will enable higher processing density and more sophisticated AI acceleration capabilities within mobile form factors.
Federated Learning Integration
Federated learning represents a promising approach for combining the privacy benefits of edge AI with the learning capabilities of distributed systems. Future implementations will enable smartphones to collaboratively train AI models while keeping personal data local. This approach could significantly improve model accuracy and capabilities while maintaining privacy protection.
Edge-cloud hybrid architectures will provide seamless transitions between local and remote processing based on current requirements and constraints. These systems will intelligently distribute AI workloads between edge and cloud resources, optimizing for factors such as latency, privacy, power consumption, and accuracy requirements.
Conclusion
Edge AI architecture represents a transformative approach to mobile artificial intelligence that addresses fundamental limitations of cloud-based solutions while enabling new categories of intelligent applications. The integration of specialized neural processing units, optimized software stacks, and sophisticated model deployment strategies creates powerful platforms for on-device AI processing.
The benefits of edge AI extend beyond technical performance improvements to include enhanced privacy protection, reduced network dependency, and improved user experience through low-latency processing. As hardware capabilities continue to advance and optimization techniques become more sophisticated, edge AI will enable increasingly powerful and intelligent mobile applications.
However, significant challenges remain in balancing resource constraints with AI capability requirements. Future developments in hardware architecture, software optimization, and hybrid edge-cloud approaches will be essential for realizing the full potential of edge AI in smartphones. The continued evolution of this architecture will play a crucial role in shaping the future of mobile computing and artificial intelligence integration.
The success of edge AI architectures will ultimately depend on their ability to provide compelling user experiences while addressing privacy concerns and resource limitations. As these systems mature, they will likely become the foundation for a new generation of intelligent mobile applications that seamlessly integrate AI capabilities into everyday smartphone usage, transforming how users interact with their devices and access intelligent services.
Discover more from SkillWisor
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
